
windowSafe® special sealing gaskets
made of cell rubber, sponge & soft rubber, high performance foam and other materials
windowSafe® is your expert for special sealing gaskets and cushions: made from a variety of materials and for a wide range of industries. Many years of experience in the sealing sector enable us to develop and manufacture specific and customized products according to our customers' wishes - from initial batches to large runs.
Discover and use the windowSafe® options such as individual advice and support, custom-made products, state-of-the-art manufacturing techniques and a whole range of additional services (e.g. packaging).
Special sealing gaskets at a glance
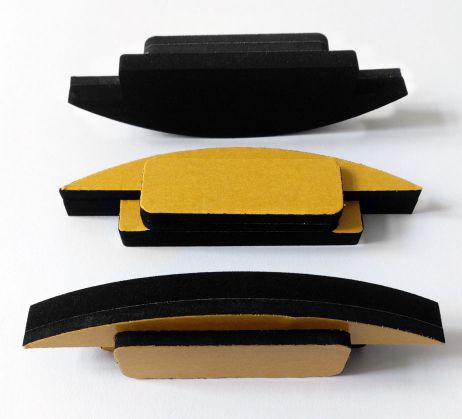

Special seals made of cell rubber
Seals and sealing cushions made of cellular rubber are a windowSafe® core competence.
Most cellular rubber qualities are closed-cell, soft and elastic and therefore ideal for sealing purposes. The material can be split, cut, punched and glued. In addition it can be coated, perforated, laminated and processed into most types of seals:
- 3D special gaskets
- classic sealing cushions for windows & facades
- flat gaskets with or without self-adhesive
In addition cell rubber sealing gaskets and cushions can be manufactured quickly and cost-effectively even in small quantities. There are no tool costs in principle.
Send your request for a cell rubber gaskets with a drawing to: info@windowsafe.de.

Seals made of sponge & soft rubber
Other rubber materials - namely sponge rubber and soft rubber - are also used in the sealing area.
Among the soft rubber qualities EPDM is particularly popular. The material is available in Shore hardness from 20° to 85° (Shore A). EPDM is very resistant to weathering and ageing. It has high elasticity and good cold behaviour. EPDM seals are used primarily in the automotive industry but also in the construction sector.
In contrast sponge rubber is a celled rubber material but with a mixed-cell structure. It has high compressive elasticity and good resilience. The material is often used for round cords and profiles but can also be used for seals and sealing cushions.
Request your special seal made of soft rubber or sponge rubber with a drawing: info@windowsafe.de.
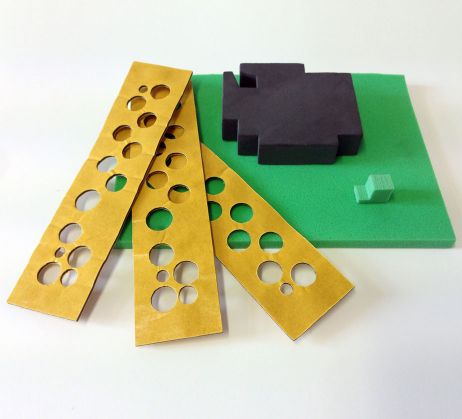

Seals made of high performance foam
In addition to rubber materials such as cell or sponge rubber foam is of course also available for sealing tasks.
In the area of high performance foam the choice of materials is huge. A wide range of application forms and functions can be covered. A small selection:
- PE foam = low thermal conductivity, particularly cost-effective
- silicone foam = highly temperature resistant, suitable for foodstuffs
- melamine foam = highly temperature resistant, very light, excellent sound-insulation properties
- Sylomer® = particularly robust, highly abrasion and wear resistant
You are not sure which material is suitable for your special seal?
Send your request to: info@windowsafe.de.
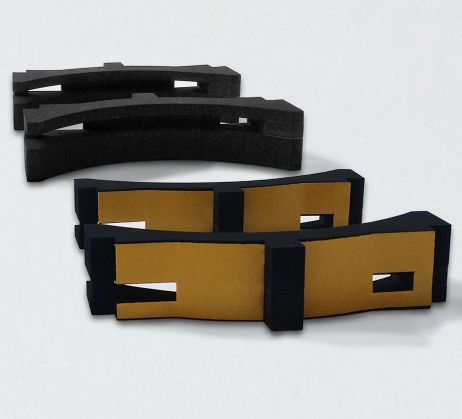

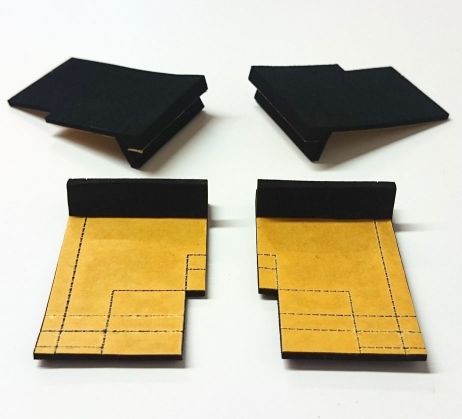
3D sealing gaskets
Manufacturing gaskets with a 3D geometry is often complex and technically demanding.
Some 3D seals can be produced using a 3D water jet cutter. In other cases a blank undergoes several operations or separate individual parts are glued together. In particularly complicated cases all three manufacturing processes will be combined.
Examples of cell rubber sealing gaskets that require 3D manufacturing:
- Seals need to have self-adhesive coating on partial surfaces.
- Sealing gaskets need undercuts or recesses.
- Seals need to be equipped with holes to make later assembly easier.
Send us your request for a 3D sealing gaskets with a drawing: info@windowsafe.de.
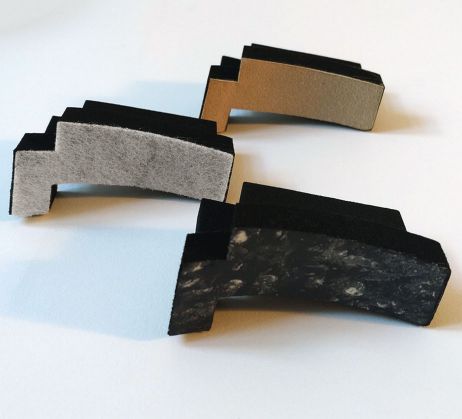

Coated sealing gaskets
The existing properties of a material can be supported and expanded through coating. When it comes to sealing gaskets an improvement in either temperature resistance or lubricity is often desired. This is particularly the case with celled materials such as cellular rubber.
Temperature resistance: to optimize temperature resistance a coating with PTFE is recommended. The material is applied in a liquid state and forms a thin, flexible outer skin that can withstand very high temperatures without affecting the sealing function.
Lubricity: the coating with liquid PTFE can also be used for improved sliding properties. In addition partial coating with solid materials is possible (e.g. solid PTFE, rubber, plastic, felt, etc.). Placed in strategic locations they prevent excessive friction between the seal and the operating environment.
For more coating options please contact us: info@windowsafe.de.
Perforated sealing gaskets
Perforated sealing gaskets are the all-purpose tool among sealing products.
Instead of two, three or more different seal geometries only one geometry is manufactured and fitted with perforations. During assembly the seal that is needed is "made" by detaching parts that are not required.
However bevor fitting sealing gaskets and cushions with perforations the following points should be taken into account:
- The material should be suitable for perforation (e.g. cell rubber).
- The seal should not be too thick so that the perforation still works.
- Please check whether thick perforation cuts may affect the tightness of the sealing gasket.
Any questions? Please feel free to contact us: info@windowsafe.de.

Seals for special technical applications
Special sealing gaskets are the windowSafe® standard. But sometimes more is needed.
Whether in the food sector, refrigeration technology or fire protection - technically demanding environments require not only special production methods but also special materials.
windowSafe® seals for special technical applications:
- special seals with food approval
- special seals with fire protection properties (flame resistant, self-extinguishing, etc.)
- special seals for refrigeration & air conditioning technology (highly temperature-resistant)
- special seals partially made of renewable or recycled raw materials
Challenge us. We will also find the right solution for you.
Technical information
Many materials used for sealing can be split, milled, cut, punched, glued and water jet cut.
However it should be kept in mind that there are differences between the processing of cellular materials, elastic solid materials and solid materials such as HD plastic. Even if the same processes can be used there are usual differences in dimensional accuracy and tolerances.
The most important manufacturing processes briefly explained:
Splitting
By splitting the raw material - which often comes in blocks or plates - is cut to the processing thickness. For example a cell rubber sheet with dimensions of 1,000 x 1,000 mm and a thickness of 40 mm can be split into 4 sheets with dimensions of 1,000 x 1,000 x 10 mm. Since product thickness varies greatly splitting is often the first step in the manufacturing process.
Punching
Punching (also called die cutting) is a manufacturing method that is primarily used for flat gaskets. Here a metal cutting die is made first. The die is pressed through the material. This creates parts in the desired shape. The resulting cutting edges are – unlike with water jet cutting – free of grooves. However slight concavity may occur with larger material thicknesses.
Water jet cutting
During water jet cutting the material is separated by a high-pressure water jet. Since the contours can be programmed directly into the machine there are no costs for tools or molds. Even complex contours are no problem. In contrast to punching concave cutting edges are not created with larger material thicknesses. However grooves can form on thicker materials due to the jet breaking out.
Cellular rubber, sponge rubber and solid rubber are all processed forms of rubber. All three materials are made from the same raw materials (e.g. EPDM).
The main differences lie in the cell structure and correspondingly in the processing options.
Cell structure
Cellular rubber and sponge rubber are foamed using blowing agents and are therefore often referred to as foam rubber. While cellular rubber usually has closed cells, foam rubber is a mixed-cell material.
In order to seal optimally, foam rubber needs a closed outer skin. If this is damaged, it will affect the sealing function. Cellular rubber, on the other hand, is tight even without an outer skin. During processing, the external cells are cut, but water cannot penetrate further into the material. The surface made of cut cells also has advantages: it is non-slip and well suited for bonding with adhesives. For this reason, cellular rubber is often preferred in the sealing sector.
Solid rubber, on the other hand, is - as the name suggests - a solid material that has no cells. For this reason, solid rubber is usually used for other types of seals: e.g. for mechanical or flat seals.
Processing
All three materials can be split, cut and punched. Seals and sealing cushions are cut or punched out of raw material in block or plate form.
Unlike cellular rubber, solid and foam rubber can also be shaped directly: for example by extrusion. The raw material is pressed (extruded) through a shaping opening and a profile with the corresponding cross-section is created. Since cellular rubber is not extruded, cellular rubber profiles are usually foam rubber profiles.
Celled rubber types compared
Special sealing gaskets made of cell rubber
- excellent sealing properties
- low thermal conductivity
- excellent compressibility
- good insulation properties
- vacuum water absorption <5% (without outer skin )
Special sealing gaskets made of sponge rubber
- high compressive elasticity
- high compressibility
- good insulation properties
- flexible processing options (i.e. extrusion)
Cellular rubber is a foam-shaped elastomer that is primarily used for sealing, insulating and providing buffering. Since the material has cells that are closed on all sides water and air impermeability of up to 99.9% can be achieved.
The technical properties of cellular rubber at a glance
- excellent sealing properties
- low thermal conductibility (ca. 0,04 W/mK)
- excellent compressibility
- excellent insulation properties
- very low water absorption
- flexible processing options
- high ageing and temperature resistance (EPDM)
- high flame retardancy and oil resistance (CR/NBR)
What makes cellular rubber so special as a material is its closed cells. It is therefore preferably used where something needs to be permanently sealed, for example in windows and facades or in mechanical engineering. Its popularity as a material for sealing gaskets and cushions has led to a variety of cellular rubber qualities that can do much more than just seal. There is:
- a wide range of material hardness: from super soft (10° Shore 00) to hard (80° Shore 00)
- food-grade cell rubber qualities
- self-extinguishing cell rubber qualities
- temperature resistant cell rubbers
- qualities with a variety of certifications & approvals (UL94, FMVSS, ISO, REACH, etc.)
Even sustainable cellular rubbers are slowly coming onto the market - i.e. qualities that are made from renewable raw materials, contain recycled content or are easily recyclable themselves.
Polyethylene foam (or PE foam) is also known as cell polyethylene, Plastazote or LD29.
Thanks to a range of technical advantages PE foam is often used in sealing applications. These include excellent insulating properties, good chemical resistance, physiological harmlessness and low cost. In addition there are food-safe, flame-retardant, electrically conductive, static dissipative and super soft polyethylene foam types.
Technical properties of PE foam
- variable density (from 15 kg/m³)
- low thermal conductivity (ca. 0,04 W/mK)
- high chemical resistance
- low in fogging and allergies
- high ageing resistance
- thermoformable
- flame retardant (LDFR)
- available in various colours
- electrically conductive or antistatic
- flexible processing options
- cost-effective
Like sponge or soft rubber PE foam can also be extruded. Extruded PE foam profiles are used for insulation, sealing or as filling.
You are interested in PE foam profiles? Then visit our product section "Extruded PE foam profiles".
Polyurethanes (PU or PUR for short) are “everyday special plastics” whose annual usage is several million tons. As with polyethylene a distinction is made between PUR foams and cell-free PUR materials.
High-performance PUR foams have similar elastic properties to cellular rubber materials but surpass them with excellent wear behaviour and high tear resistance. Many of these foams are known by their trade names, e.g. Cellasto®, Vulkollan® or Sylomer®.
PUR foam Vulkollan®
- excellent mechanical wear resistance
- high impact elasticity
- low compression set
- good resistance to mineral oils, fats and gasoline
- good solvent resistance
PUR foam Cellasto®
- excellent springing and damping properties
- high volume compressibility with low transverse strain
- low compression set
- high abrasion resistance
- very good static & dynamic long-term behaviour
- temperature range from -30°C up to +80°C
- good chemical resistance
However it should be noted that many high-performance foams are mixed-cell or even open-cell materials and therefore do not seal reliably. Cellular rubber is usually more suitable for pure sealing purposes.


